Patterns in Google Review Deletions
This article is a research done on the GMBapi.com customer base. It is based on nearly 5 million reviews across 78 countries and over 19,000 locations. While the first instance of a deleted review (in our system) occurred in September 2024, the dataset includes reviews dating back to January 2011, which is when the earliest deleted review was created.
Online reviews are crucial in shaping a business’s reputation and financial performance. But what happens when these reviews disappear? A striking number of reviews are removed by Google, leaving businesses and customers questioning the underlying reasons. To uncover the patterns behind these deletions, we analysed a large dataset from thousands of business locations across various industries.
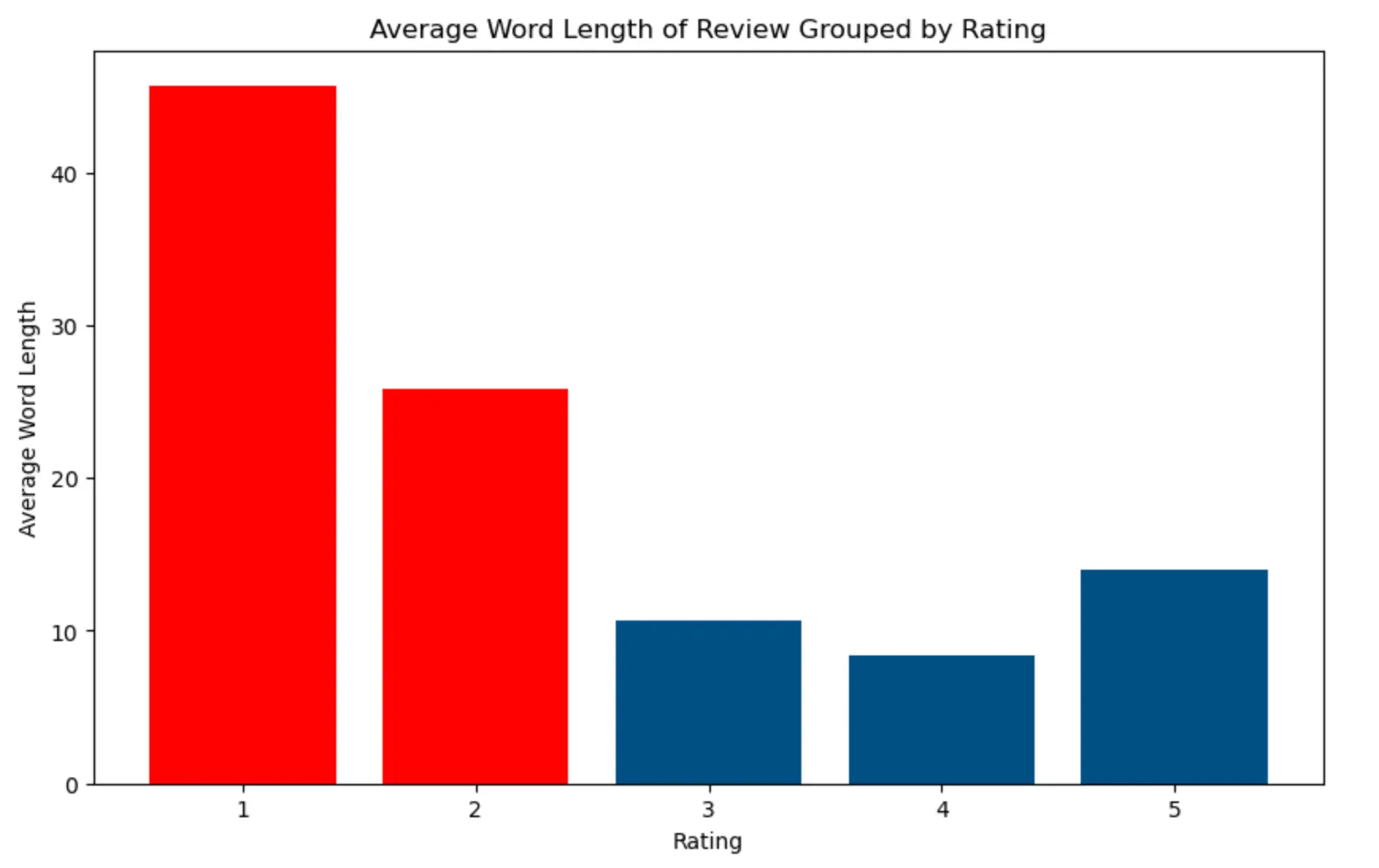
Here’s what we know about reviews so far: Negative reviews – those rated 1 or 2 stars – are often longer, as unhappy customers tend to go into detail about their experiences. But how do factors like the review’s tone, timing, content, and even the way you respond, impact the chances of getting it deleted? Let’s explore the data and find out.
Time-Based Trends of Deleted Reviews
Trends in Deleted Reviews Over Time
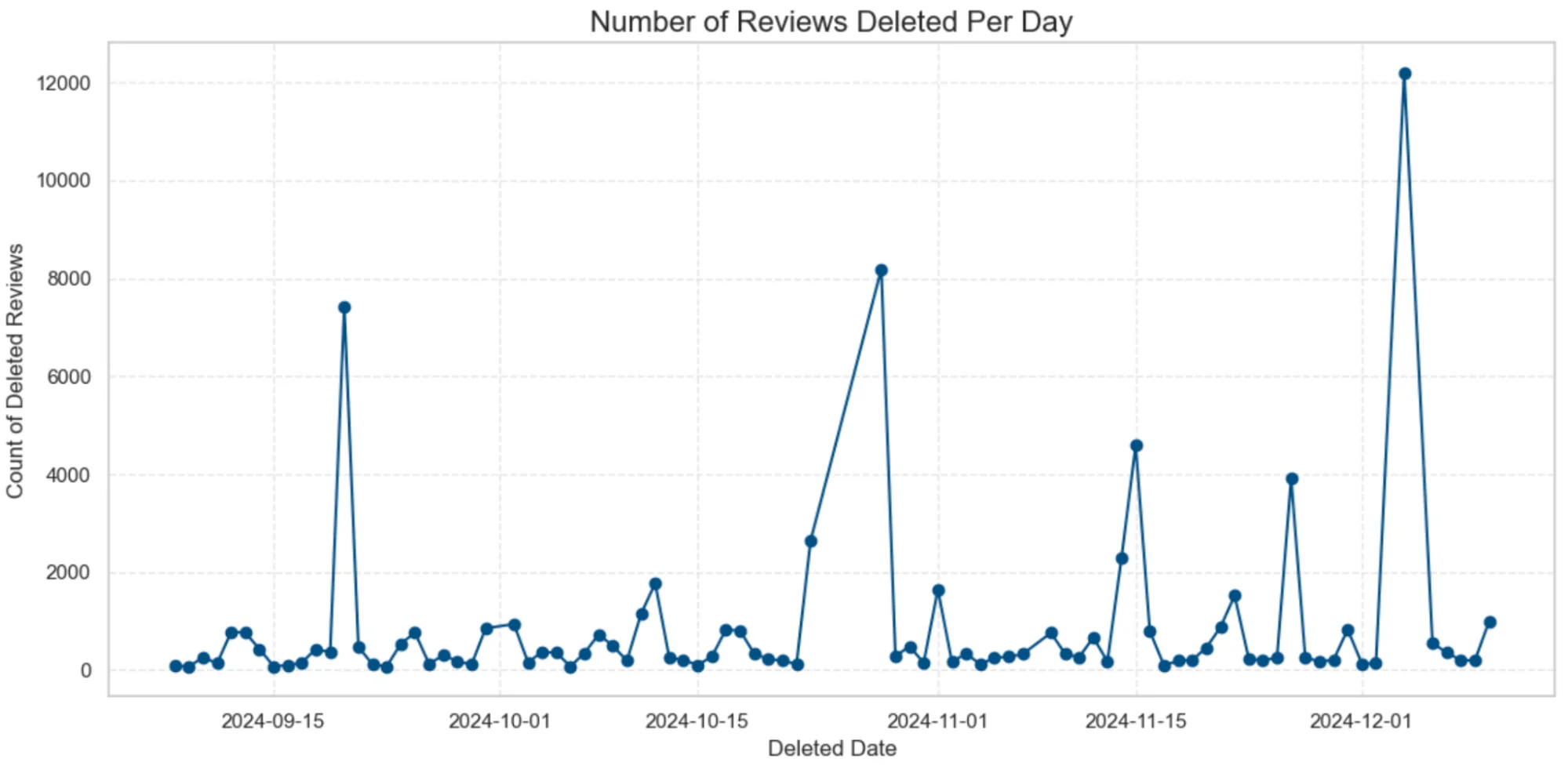

The graph above shows the number of reviews deleted per day over several months. We noticed spikes around mid-September, late October, and early December, which could indicate mass deletions, possibly due to policy enforcement or automated spam detection systems.
In September 2024, Google rolled out the Helpful Content Update, which focused on putting user-friendly content front and centre while cracking down on spammy or low-quality material. This likely included stricter checks on reviews that seemed fake or misleading. Furthermore, the Spam Update came into play in late October 2024, targeting spam across the board, including reviews. That could explain why there was a wave of mass deletions around that time. Lastly, Google launched the November Core Update in November–December 2024, which was all about improving search result quality. It likely hit reviews that didn’t meet Google’s standards for trustworthiness or authenticity. These kinds of updates often result in large-scale removals of content like fake reviews.
Review Deletions by Day of the Week
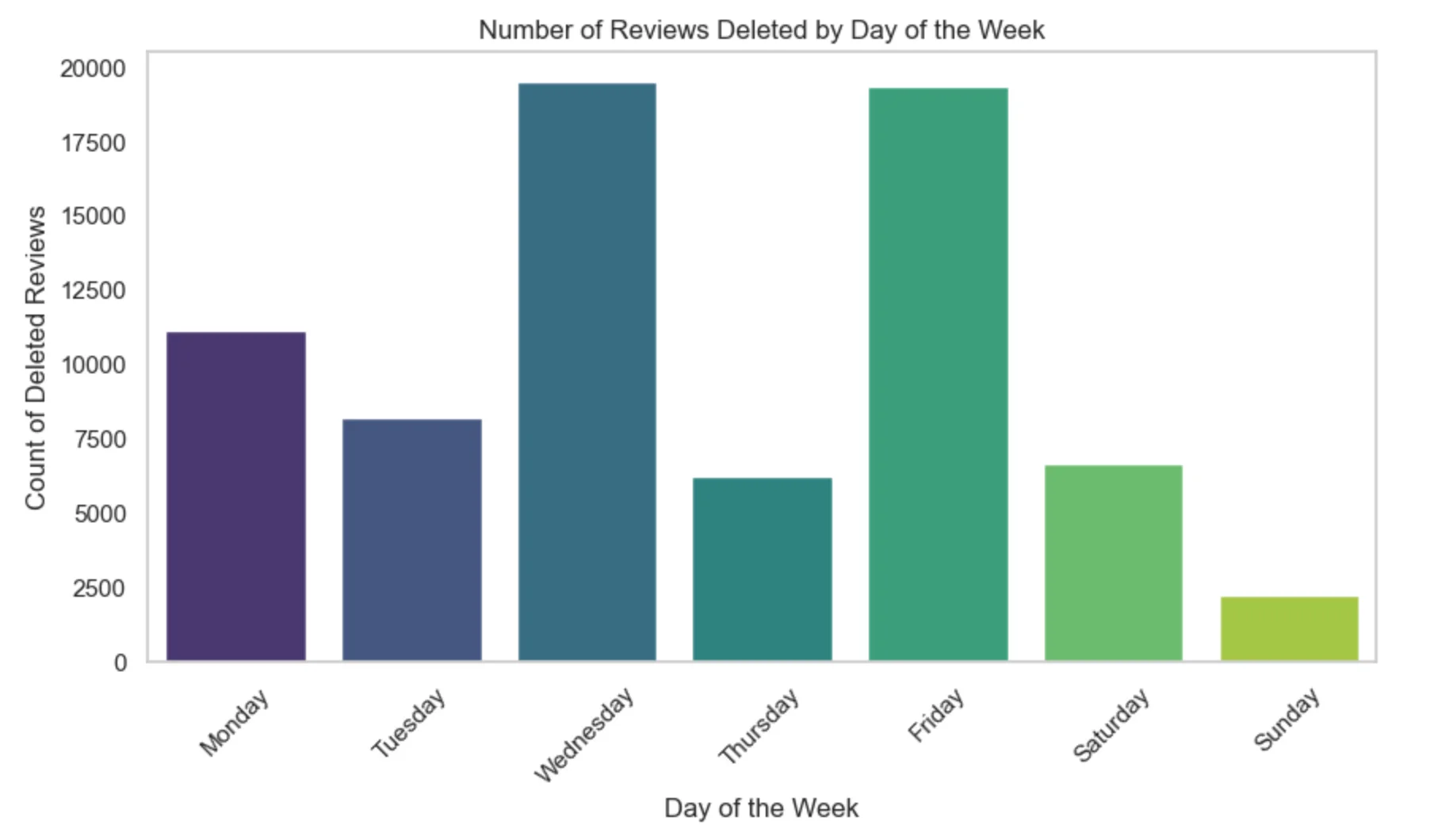

The second graph shows review deletions by day of the week. Deletions were highest on Wednesdays and Fridays, while Sundays had the lowest activity. This trend likely reflects Google’s operational patterns, with less manual moderation occurring over the weekends.
Ratings and Replies of Deleted Reviews
Ratings and business replies provide valuable context for understanding patterns in deleted reviews. Here’s what the data reveals about their role in Google’s moderation process.
Rating Distribution of Deleted Reviews
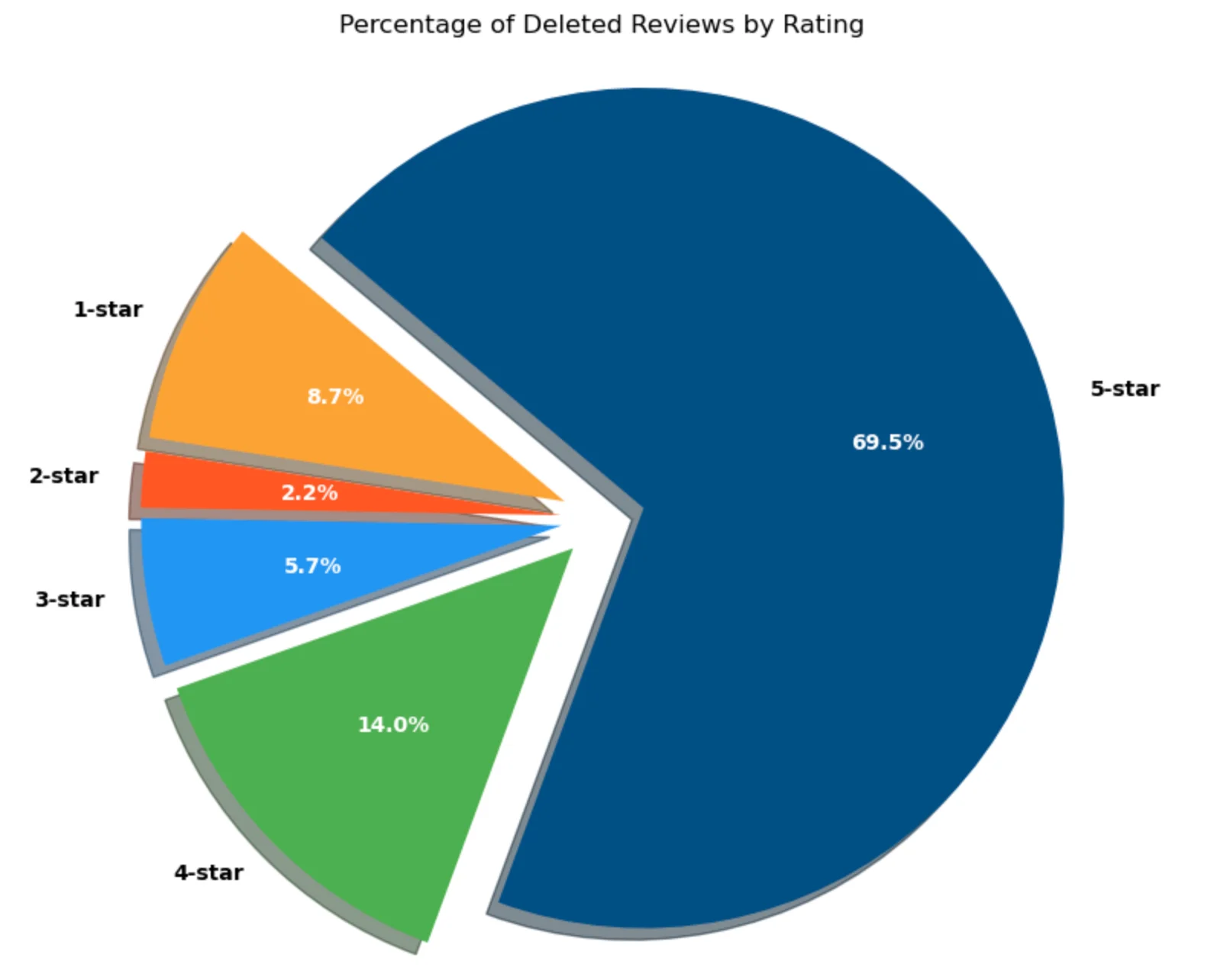

The updated pie chart shows the distribution of deleted reviews by rating. An overwhelming 69.5% were 5-star reviews, followed by 14% for 4-star reviews.
The high percentage of 5-star reviews being deleted suggests Google is actively targeting potentially fake or incentivised positive reviews, which might skew business reputations. Lower-rated reviews (1 or 2 stars) account for a smaller proportion, indicating these may not be as frequently flagged unless they violate specific policies.
Do Replies Impact Deletions?
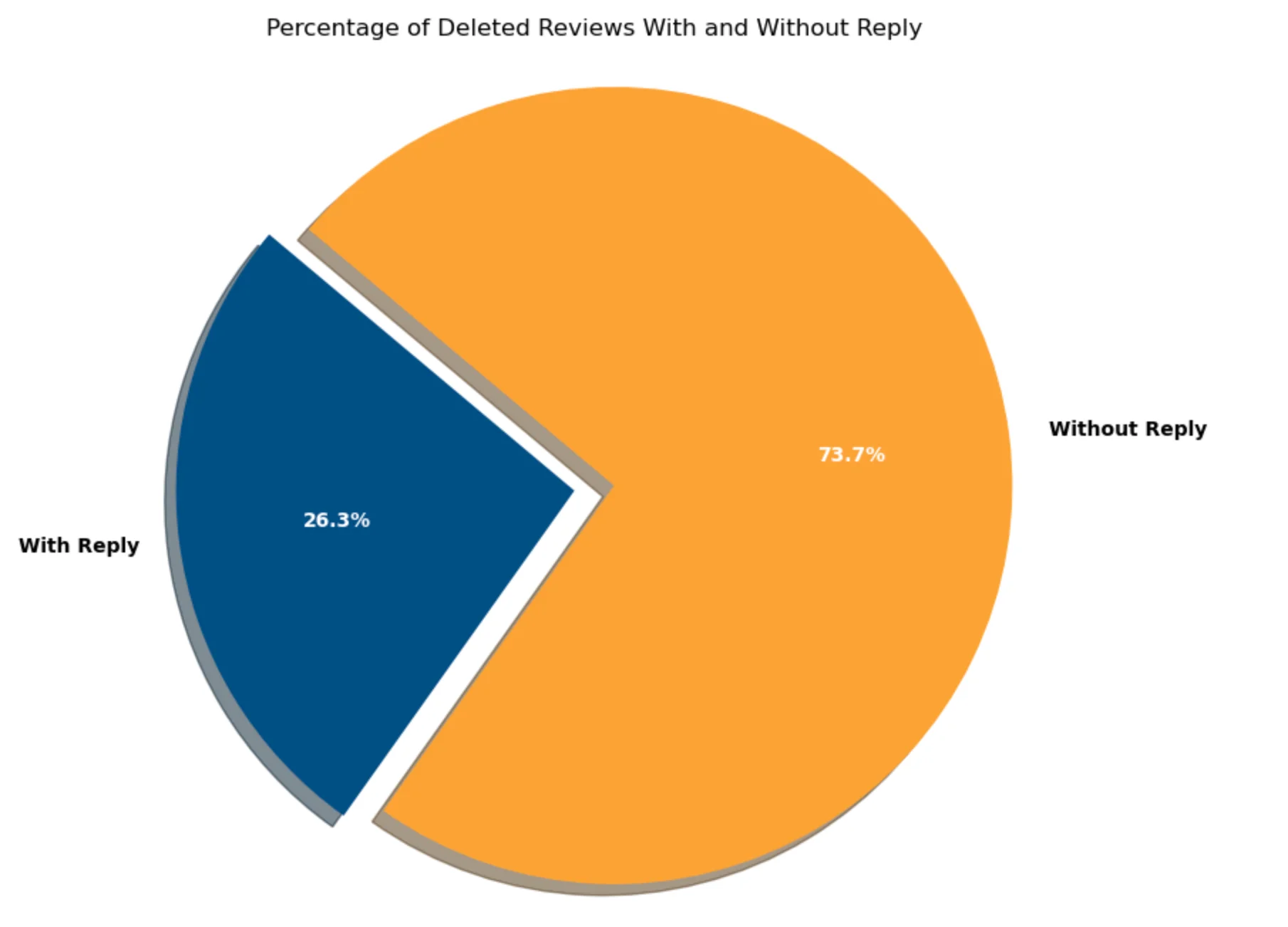

Our data reveals an interesting trend: 73.7% of deleted reviews had no business replies, while 26.3% did. This suggests that engaging with reviewers might help reduce the chances of deletion. However, replies alone aren’t a foolproof safeguard, Google’s algorithms seem to focus more on the quality and authenticity of the review content itself.
Sentiment Analysis of Deleted Reviews
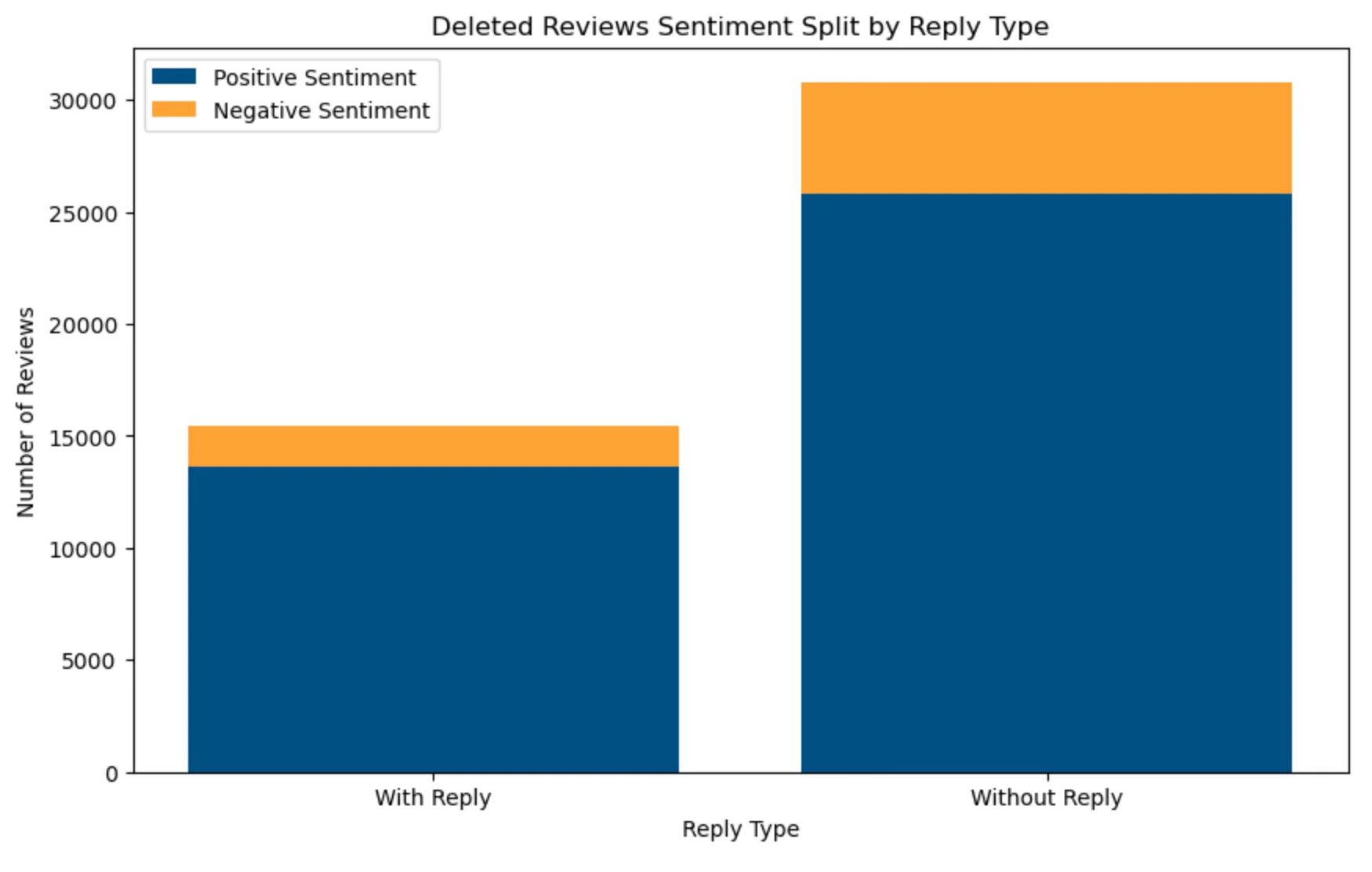

A significant portion of positive reviews without replies are removed, possibly indicating the detection of inauthentic or incentivised reviews.
Deleted vs. Non-Deleted Reviews
By comparing deleted and non-deleted reviews, we can uncover whether or not there are noticeable differences between the two. This analysis provides insights into whether certain patterns or extremes make reviews more likely to be removed.
Ratings
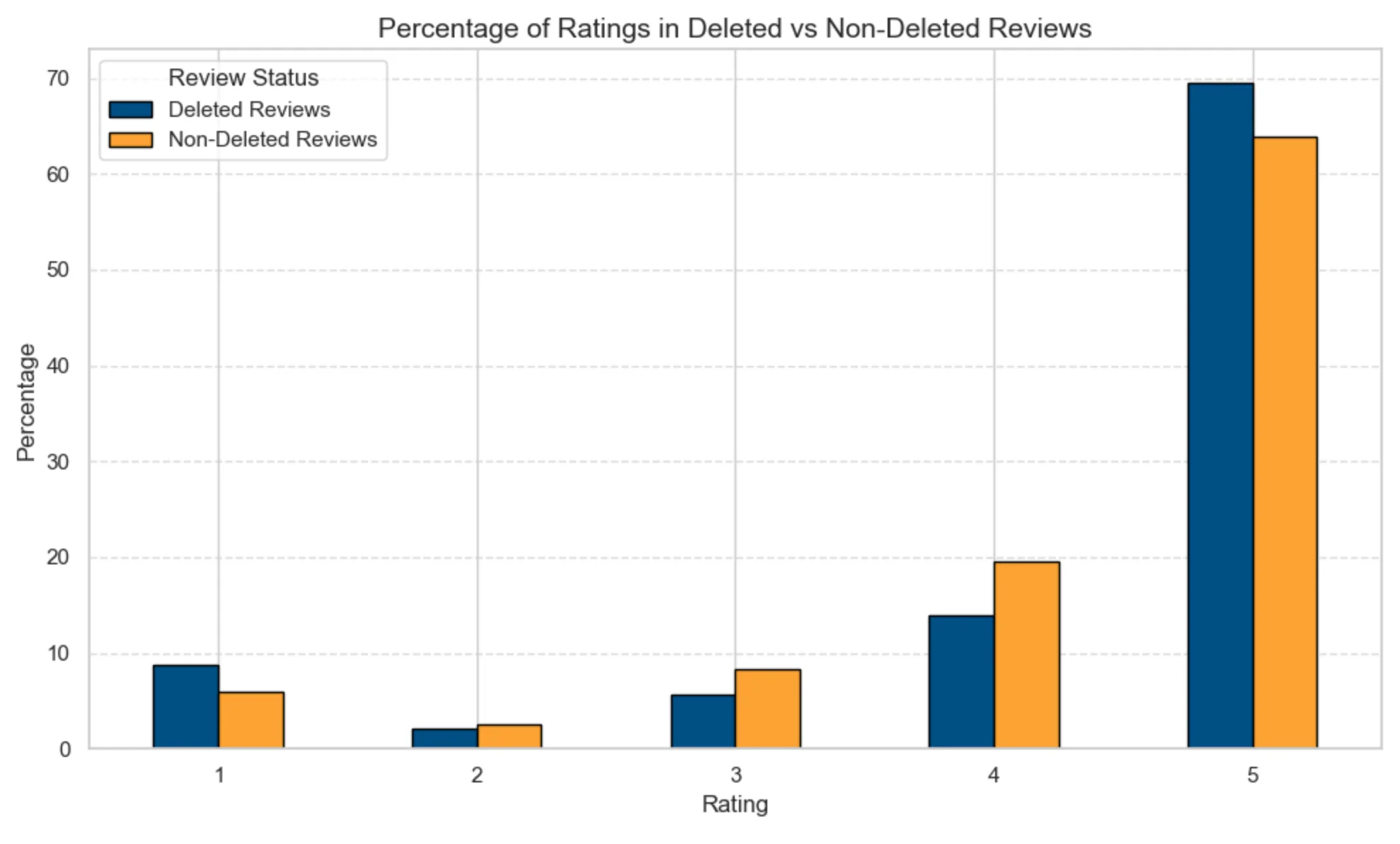

Google targets extreme ratings, with 5-star and 1-star deleted reviews containing a higher percentage than non-deleted reviews. While 5-star reviews are scrutinised for fake or rewarded content, 1-star reviews are often removed for offensive language or spam. This highlights Google’s focus on moderating impactful reviews at both ends of the spectrum.
Categories and Themes in Deleted Reviews
The content of a review appears to be a key factor in whether it gets removed. To investigate this, we conducted a detailed analysis of the content and keywords most commonly found in deleted reviews.
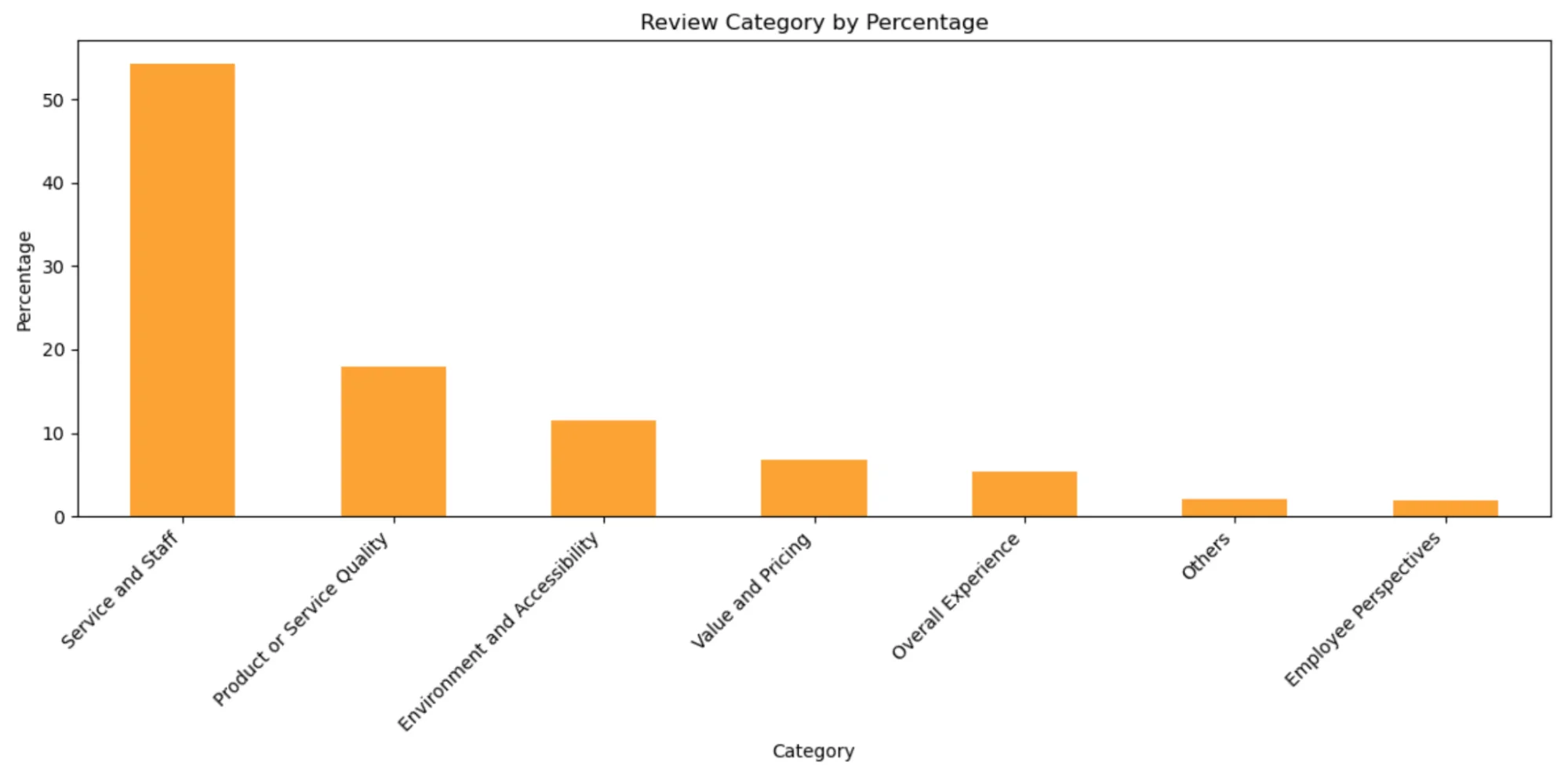
Review Categories

| Category | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Service and Staff | Comments about customer service quality, staff friendliness, expertise, or responsiveness. |
| Product or Service Quality | Comments about the quality, reliability, or performance of products or services offered. |
| Value and Pricing | Comments about affordability, perceived value, or whether the price matches the experience. |
| Environment and Accessibility | Comments about cleanliness, ambiance, location, convenience, or accessibility. |
| Overall Experience | Comments about the general experience, problem resolution, or satisfaction with the business. |
| Employee Perspectives | Comments written by current or former employees about workplace conditions, management, or company culture. |
| Others | Comments that are not related to the topics above. |
The bar chart highlights the categories most commonly associated with deleted reviews, with “Service and Staff” leading the way, followed by “Product or Service Quality” and “Environment and Accessibility.”
The high proportion of “Service and Staff” reviews being deleted may be tied to the volume of feedback businesses typically receive in this area. While many comments in this category are positive, they may be flagged for authenticity checks, particularly if the reviewer’s history suggests patterns of overly generic, excessively positive, or potentially incentivised feedback.
Interestingly, a portion of deleted reviews falls under “Employee Perspectives.” This indicates that Google actively removes reviews left by employees to minimise biased or self-serving feedback that could distort a business’s reputation. If you see competitors doing this, you can flag these reviews under the “conflict of interest” category and they are likely to be removed.
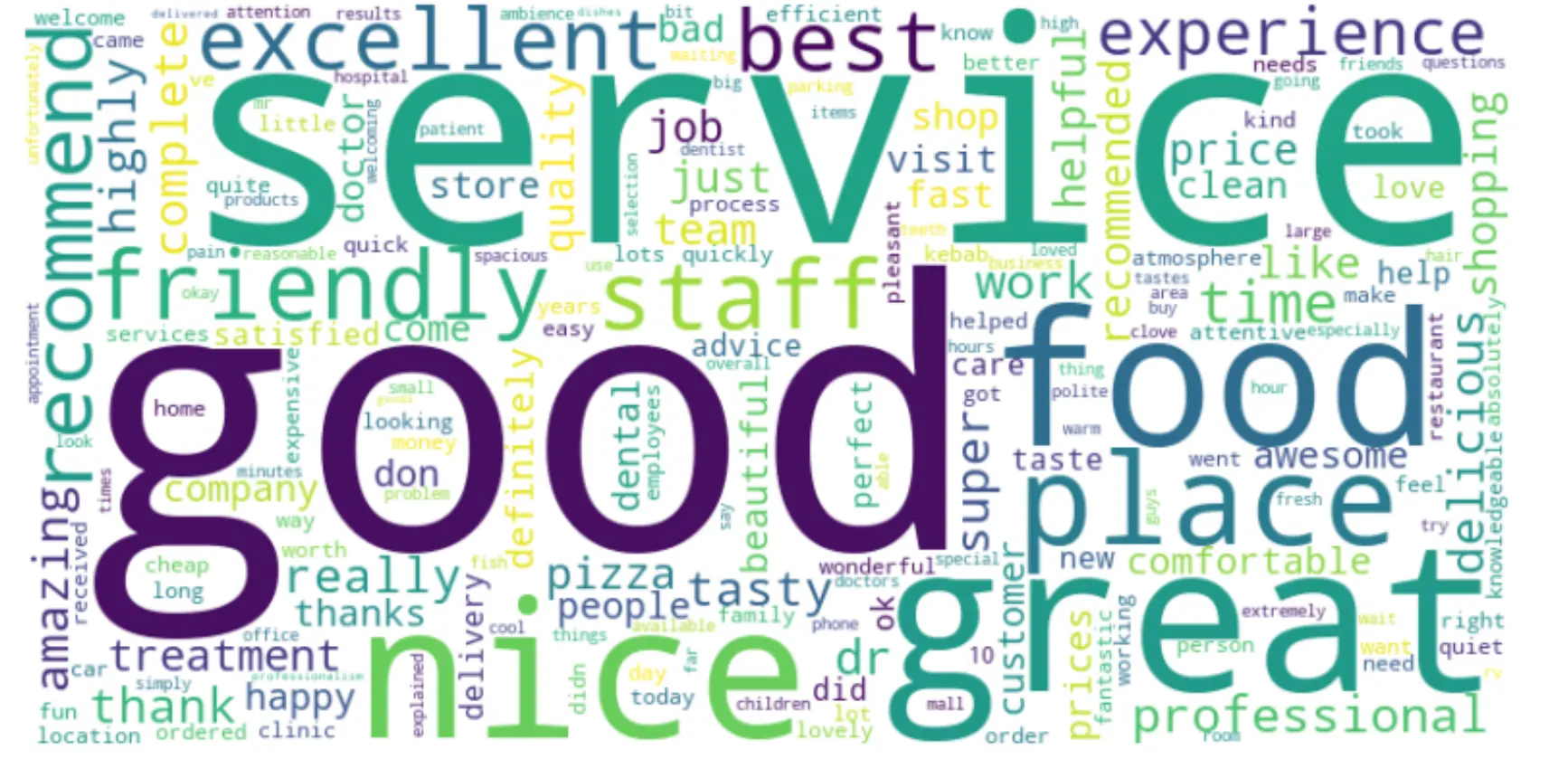
Common Words in Deleted Reviews

Machine Learning Insights
To better understand what factors influence whether a review is deleted, we developed a machine-learning model using the Random Forest algorithm. Our analysis focused only on review-specific data, as we didn’t have access to information about the reviewers themselves. The model achieved an accuracy of 61% and revealed the top four factors that play a role in review deletion:
- Sentiment: The tone of the review is measured on a scale from -1 (entirely negative) to 1 (entirely positive).
- Review Length: The total number of characters in the review.
- Word Count: The number of words in the review.
- Response Time: How quickly the business responded to the review.
While these features gave us valuable insights, we know from other research that including reviewer-specific data, like posting patterns or behaviour, can significantly improve the accuracy of detecting fraudulent or low-quality reviews.
What Other Research Shows
Studies that include reviewer-centric features, such as posting habits, have reported higher success rates in identifying fake or problematic reviews:
- How to Detect Fake Online Reviews using Machine Learning | by Kessie Zhang – Zhang’s research highlights that the number of reviews posted by a person and the average length of those reviews are strong indicators of authenticity. As AI tools become more advanced at creating human-like text, patterns in reviewer behaviour often outperform text-based analysis in detecting fake content.
- ScienceDirect’s Research on Behavioural Metrics – This study showed that adding features like the timeframe over which a reviewer posts reviews and the total number of reviews they’ve written dramatically improves detection accuracy. These behavioural metrics help differentiate real feedback from fraudulent or incentivised reviews.
The Bigger Picture
Although our model relied solely on review-specific data, these findings underline the importance of integrating reviewer-centric features in future analyses. By combining text-based insights with behavioural data, machine learning models can become more effective at identifying and addressing fake reviews, ensuring businesses can maintain trust and credibility online.
Analysis Summary
Our findings suggest that Google’s review deletion process is driven by several key factors:
- Inauthentic Activity: Reviews flagged as fake or promotional, especially in 5-star ratings, appear more likely to be removed.
- Keyword-Based Detection: Certain repetitive or generic terms may contribute to reviews being flagged and trigger deletions.
- Content and Tone: Extreme ratings, such as overly positive 5-star or negative 1-star reviews, seem to undergo closer examination, potentially due to their large impact on a business’s reputation.
- Engagement Factors: Reviews without replies or those from suspicious users may increase the likelihood of deletion. Reviewer-centric features have proven more effective than text features for identifying fake reviews in prediction models.
Policy Enforcement: Reviews related to sensitive topics, such as employee feedback, may also be subject to moderation to ensure impartiality.
Recommendations for Businesses
To minimise the risk of review deletions:
- Engage with Reviewers: Respond promptly to both positive and negative reviews, especially positive ones, as engaging with them may reduce the likelihood of deletion.
- Deploy Local SEO Tools: Managing multiple locations can be difficult when done manually, using a review management tool and analytics can help you protect and grow your reputation.
- Avoid Incentivised Reviews: Encourage organic reviews rather than offering rewards. We have seen the first businesses being penalised and having warning displayed on their profile that “fake reviews were recently removed from this profile”.
- Monitor for Policy Compliance: Regularly review Google’s content policies and ensure that your reviews comply.
- Report Fake Reviews: Actively report spam or inauthentic reviews to Google for resolution.
With tools like GMBapi.com, businesses can efficiently track and respond to reviews, helping to protect their online reputation. By responding promptly, you not only engage with your customers but also reduce the potential negative impact of unresolved feedback. You write those review responses for potential customers that are investigating whether or not to deal with your business. Additionally, GMBapi’s software monitors all deleted reviews, providing valuable insights into which reviews Google removes from your Google Business Profiles and why. Those removed reviews can often be re-instated.
Conclusion
Google’s review deletion process highlights its commitment to maintaining a fair and trustworthy platform. While businesses may view deletions as a setback, understanding the underlying reasons can help them adapt strategies to foster authentic, policy-compliant reviews. Our analysis provides a data-driven foundation for navigating these complexities, helping businesses optimise their online reputation in an increasingly competitive digital landscape.
Take control of your reviews and enhance your online presence with GMBapi.com — a reliable solution for efficient and seamless review management!